Amplitude Of The Resultant Waveform
Amplitude Modulation- AM Waveform- Draw Modulating Signal Carrier Wave AM wave- Modulation index - YouTube. Recall from the discussion of the single-loop generator in Chapter 1 that this maximum voltage or current occurs as the loop of wire cut the magnetic flux at a 90-degree angle.

What Is The Amplitude Of Resultant Wave When Two Waves Y1 A1sin W T B1 And Y2 A2sin W T B2 Superimpose
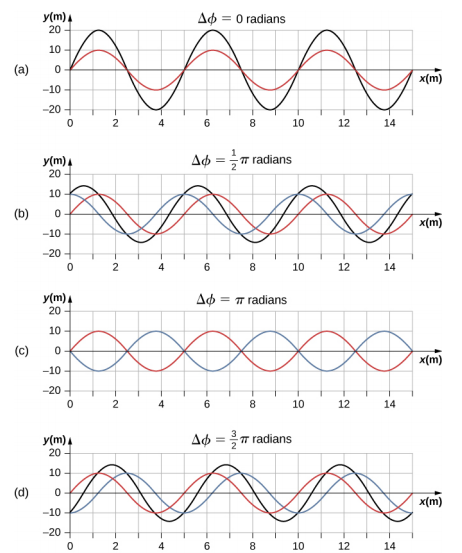
Looking now at our actual resultant wave notice that number one its amplitude doesnt seem to be constant and number two that amplitude never gets very much larger than the amplitude of any one of these individual seven or so waves.
Amplitude of the resultant waveform. Is there an error in this question or solution. The amplitude of the resultant wave produced due to the interference of the two waves is. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves for example light radio acoustic surface water waves.
This is the equation for the displacement of the resultant wave. Rather than setting the amplitude and offset of both channels independently the function generator will keep track of your settings for you. Figure 6 shows how you can control the amplitude of a square wave and a sine wave using only one amplitude setting.
Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. If you have found this video lecture useful Im happy to announce that I have created the following courses following the same style of teaching. When crest meets trough then.
A sqrt A_122A_1A_2cosA_22. You can even couple signals of different waveform shapes. This addition after all.
Below is the harmonic series and amplitudes for a Square. Resultant wave is A 1 A 2 2A. This produces a resultant waveform with differing amplitude frequency and envelope to the original waveforms.
High quality example sentences with amplitude of the waveform in context from reliable sources - Ludwig is the linguistic search engine that helps you to write better in English. ANGLE 61 ALLIE PHVID3. The amplitude of the.
The resultant amplitude A is given by squaring and adding equations 1 and 2. These effects are easily seen by adding two sine waves together each having the same steady amplitude but differing slightly in frequency. The displacement of the interfering light waves are y1 4sintand y2 3sint2.
The resultant harmonic series would also be the sum of the harmonics. The resultant waveform is simply the sum of the waveforms ie both added together. Peak Amplitude Specifications The peak amplitude of a sinusoidal waveform is the maximum positive or negative deviation of a waveform from its zero reference level.
If two waves having amplitudes 2Aand Aand same frequency andvelocity propagate in the same direction in the same phase the resulting amplitude will be. A 2 cos 2 A 2 sin 2 A 1 A 2 cos 2 A_22 sin 2 . In physics interference is a phenomenon in which two waves superpose to form a resultant wave of greater lower or the same amplitude.
Cos 2 0 and. When two sinusoidal waveforms of different frequency are added together then because the peak and troughs positions of the two waveforms do not coincide wave interference occurs. Some synthesizers only have onoff switches for its various selectable waveforms.
It has the same frequency as that of the interfering waves. The amplitude of the resultant wave is 0 The wave are out of phase. Figure 1 shows an example waveform.
An alternating voltage e200 sin 314t is applied to a device which offers an ohmic resistance of 20 ohm to the flow of current in one direction while preventing the flow of current in opposite direction. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave. Because of the irregular displacement of this resultant wave its not likely to have resulted from the addition of all of these waves in group one.
Average value of current. Switching on two or more waveforms will produce a new waveform based on the sum of the parts. The waves are in phase Destructive Interference.
In cases where the superposed waves have closely matched wavelengths and amplitudes for example 400 and 430 nanometers the resultant waveform displays several harmonics including the classical beat frequencies so commonly observed in sound waves.

Two Waves That Add To Give A Resultant With The Same Amplitude Youtube
16 6 Interference Of Waves Physics Libretexts

16 5 Interference Of Waves University Physics Volume 1

Superposition And Interference Physics

Two Waves Having Equation S X 1 Asin Omegat Phi 1 X 2 Asin Omegat Phi 2 If In The Resultant Wave The Frequency And Amplitude Remain Equal To Those Of Superimposing Waves Then Phase Difference Between Them Is
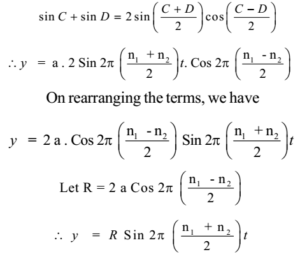
Formation Of Beats Meaning Of Beats Expression For Period And Frequency
Two Waves Of The Same Frequency And Same Amplitude Are Reaching A Point Simultaneously What Should Be The Phase Difference Between The Waves So That The Amplitude Of The Resultant Wave Is 2a

16 5 Interference Of Waves University Physics Volume 1

Principle Of Superposition Of Wave Resultant Intensity Superposition Superposition Of Waves Youtube

Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Of Two Waves In Wave Optics For Jee And Neet Youtube
Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Myrank
Adding Waves Of The Same Frequency Together

Random And Coherent Sources Ppt Download

Two Waves Represented By Y A Sin W T Kx And Y A Cos W T Kx Are Superposed The Resultant Waves Will Have An Amplitude

The Resultant Amplitude When Two Waves Of Two Waves Of Same Frequency But With Youtube

The Resultant Amplitude Of Two Superposed Waves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Two Sinusoidal Waves Of The Same Frequency Travel In The Same Direction Along A String If Y M1 3 0 Cm Y M2 4 0 Cm F 1 0 And F 2 P 2 Rad


Post a Comment for "Amplitude Of The Resultant Waveform"